Plotting information on the eigenvalues of a matrix
Samuelson's chart 2 helps us understand the behavior of his model economy, by displaying combinations of parameters for which the solution contains: (i) real or complex components; and (ii) stable or unstable components.
His dynamic model is
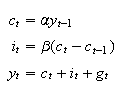
which can be cast in state-space form,
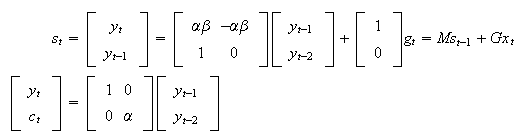
with an identity being used to determine ![]() .
.
The program samuelson.m shows how to determine the eigenvalues of this model, as well as drawing chart 2 from Samuelson's paper. In a more complicated model, it might not be possible to analytically determine how various parameter values led to qualitative behavior, but a similar computational and graphical approach could be used to view the implications of alternative parameter values.
|
% samuelson.m |
Comments |
|
%
Program Component 1: Find Roots of %
System for specific parameter values % Specify parameters alph=.5; bet=1.6; % Implied parameters theta1=alph*(1+bet); theta2=-alph*bet; % Define a matrix M which has the necessary form M = [theta1 theta2 1 0]; % Calculate eigenvalues mu=eig(M); % Calculate roots of z2 - theta1*z - theta2 = 0 mualt=roots([1 -theta1 -theta2]); disp('Roots of Samuelson model') disp([mu mualt]) disp(' ') disp('strike any key to continue') pause |
|
|
%
Program component 2 % Draw Samuelson's chart inc=.2; alphv=.1:inc:.9; betv=.1:inc:5; RTAB=zeros(length(alphv),length(betv)); STAB=zeros(length(alphv),length(betv)); for i=1:length(alphv); for j=1:length(betv); alph=alphv(i); bet=betv(j); % Implied parameters theta1=alph*(1+bet); theta2=-alph*bet; % Calculate roots of z2 - theta1*z - theta2 = 0 mualt=roots([1 -theta1 -theta2]); % make table with 1 if roots are complex iscomplex=(1-isreal(mualt)); RTAB(i,j)=iscomplex; % make table with 1 if roots are stable isunstable=(1-(max(abs(mualt))<1)); STAB(i,j)=isunstable; end end betvs=1:inc:5; line1=ones(size(betvs))./betvs; line2=4*betv./((1+betv).2); % plot Samuelson's curves axis([0 5 0 1]) plot(betvs,line1,'-k',betv,line2,'-') hold on % plot roots characteristics as points, excluding those where there is a % zero in either table for i=1:length(alphv); getr=RTAB(i,:)>0; gets=STAB(i,:)>0; plot(betv(getr),alphv(i)*ones(sum(getr)),'ok',… betv(gets),alphv(i)*ones(sum(gets)),'*k') end title('Samuelson chart 2') |
|